Following up on my first evaluation of +546,000 AI Overviews, I dug deeper into three questions:
- How are widespread crawl knowledge and AI Overviews associated?
- How does consumer intent change AI Overviews?
- How do the highest 20 positions break down for domains that rank in natural search and get cited in AIOs?
How Are Widespread Crawl Information And AI Overviews Associated?
Widespread crawl inclusion doesn’t have an effect on AIO visibility as a lot as sheer natural site visitors.
Widespread Crawl, a non-profit that crawls the net and gives the info at no cost, is the biggest knowledge supply of generative AI coaching.
Some websites, like Blogspot, contribute much more pages than others, elevating the query of whether or not that offers them an edge in LLM solutions.
Outcome: I puzzled whether or not websites that present extra pages than others would additionally see extra visibility in AI Overviews. That turned out to not be true.
I in contrast the highest 500 domains by web page contribution in Widespread Crawl to the highest 30,000 domains in my dataset and located a weak correlation of 0.179.
The reason being that Google in all probability doesn’t depend on Widespread Crawl to coach and inform AI Overviews however its personal index.
I then analyzed the connection between the three,000 high domains by natural site visitors from Semrush and the highest 30,000 domains in my dataset and located a powerful relationship of 0.714.
In different phrases, domains that get a number of natural site visitors have a excessive chance of being very seen in AI Overviews.
AIO appears to more and more reward what works in natural search, however some standards are nonetheless very separate.
It’s necessary to name out that just a few websites distort the connection.
When filtering out Wikipedia and YouTube, the connection goes right down to a correlation of 0.485 – nonetheless sturdy however decrease than with the 2 behemoths.
The correlation doesn’t change when taking out greater websites, solidifying the purpose that doing issues that work in natural search has a big effect on AI Overviews.
As I wrote in my earlier submit:
Rating larger within the search outcomes actually will increase the possibilities of being seen in AIOs, nevertheless it’s by far not the one issue.
In consequence, corporations can exclude Widespread Crawl’s bot in robots.txt in the event that they don’t wish to seem in public datasets (and gen AI like Chat GPT) and nonetheless be very seen in Google’s AI Overviews.
How Does Consumer Intent Change AI Overviews?
Consumer intent shapes the shape and content material of AIOs.
In my earlier evaluation, I got here to the conclusion that the precise question match barely issues:
The information reveals that solely 6% of AIOs include the search question.
That quantity is barely larger in SGE, at 7%, and decrease in dwell AIOs, at 5.1%. In consequence, assembly consumer intent within the content material is far more necessary than we’d have assumed. This could not come as a shock since consumer intent has been a key rating requirement in search engine optimization for a few years, however seeing the info is stunning.
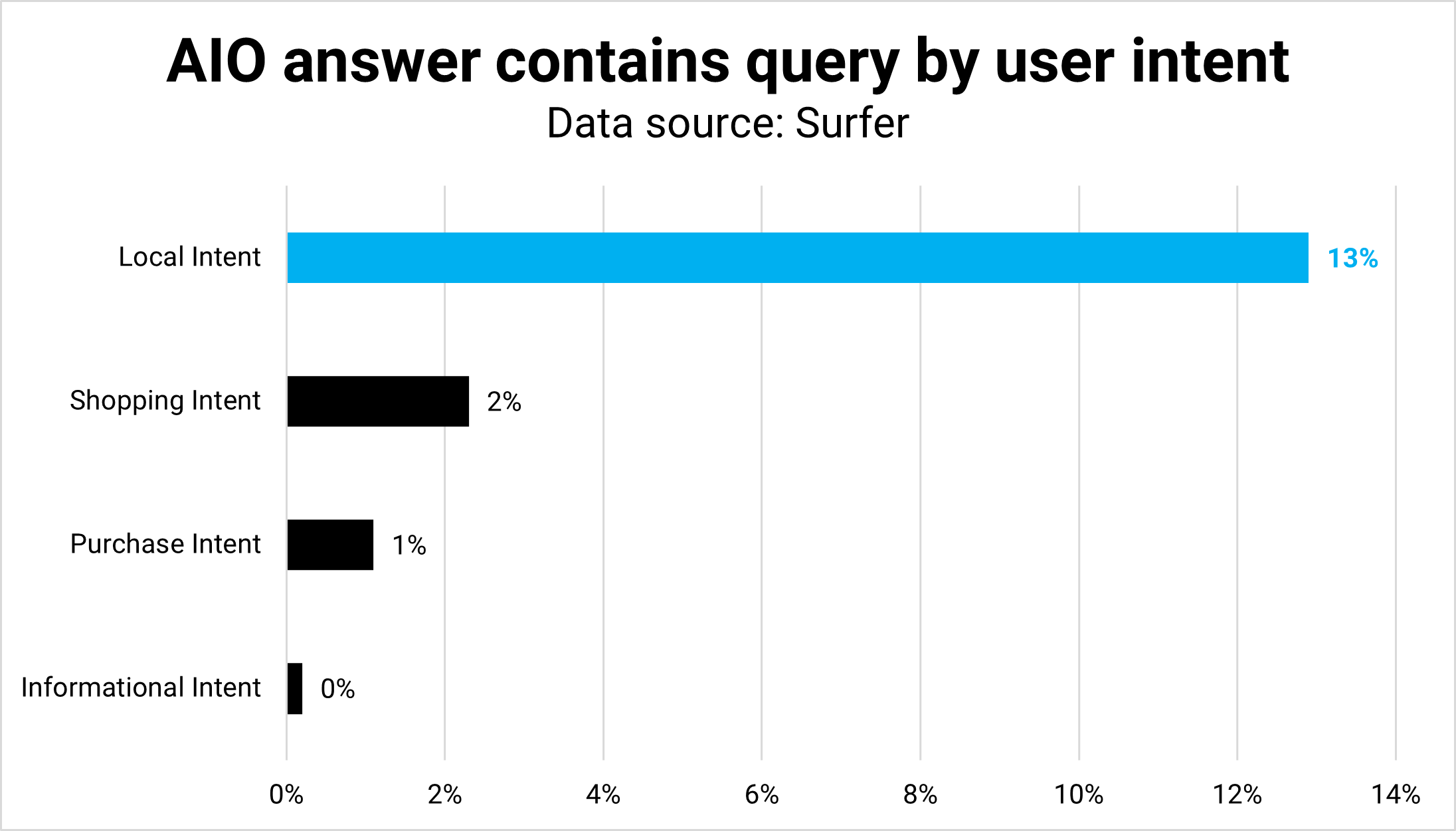
Calculating precise (dominant) consumer intent for all 546,000 queries could be extraordinarily compute-intense, so I appeared on the widespread abstractions informational, native, and transactional.
Abstractions are much less useful when optimizing content material, however they’re nice when combination knowledge.
I clustered:
- Informational queries round query phrases like “what,” “why,” “when,” and so forth.
- Transactional queries round phrases like “purchase,” “obtain,” “order,” and so forth.
- Native queries round “close by,” “shut,” or “close to me.”
 Picture Credit score: Kevin Indig
Picture Credit score: Kevin IndigOutcome: Consumer intent variations mirror in kind and performance. The typical size (phrase depend) is sort of equal throughout all intents aside from native, which is smart as a result of customers need a listing of areas as an alternative of textual content.
Equally, buying AIOs are sometimes lists of merchandise with a little bit of context except they’re shopping-related questions.
Native queries have the very best quantity of tangible match overlap between question and reply; informational queries have the bottom.
Understanding and satisfying consumer intent for questions is more durable but additionally extra necessary to be seen in AIOs than, for instance, Featured Snippets.
How Do The Prime 20 Natural Positions Break Down?
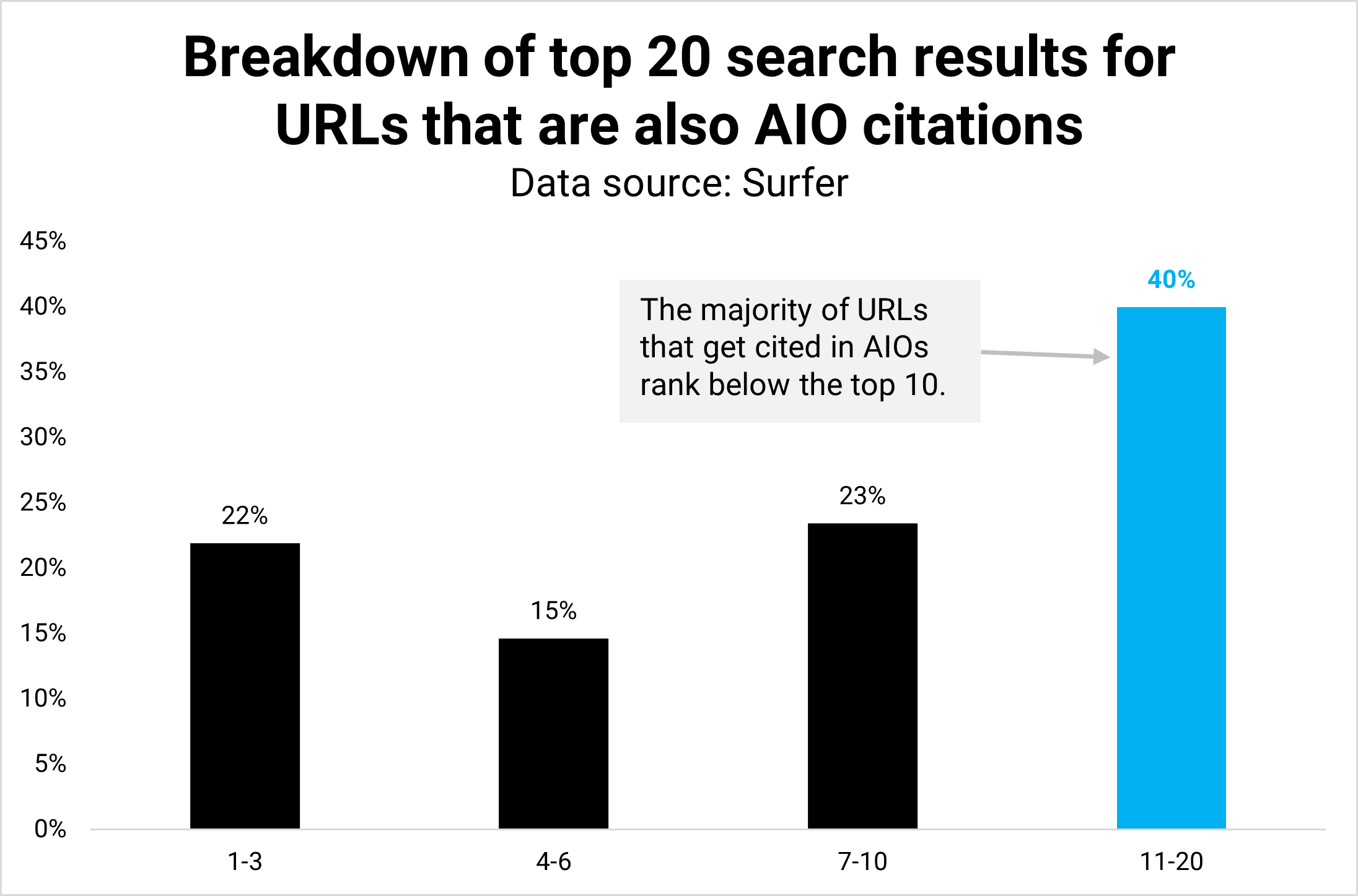
In my final evaluation, I discovered that just about 60% of URLs that seem in AIOs and natural search outcomes rank exterior the highest 20 positions.
For this Memo, I broke the highest 20 additional down to know if AIOs usually tend to cite URLs in larger positions or not.
 Picture Credit score: Kevin Indig
Picture Credit score: Kevin IndigOutcome: It seems 40% of URLs in AIOs rank in positions 11-20, and solely half (21.9%) rank within the high 3.
The bulk, 60% of URLs cited in AIOs, nonetheless rank on the primary web page of natural outcomes, reinforcing the purpose {that a} larger natural rank tends to result in a better probability of being cited in AIOs.
Nonetheless, the info additionally reveals that it’s very a lot inconceivable to be current in AIOs with a decrease natural rank.
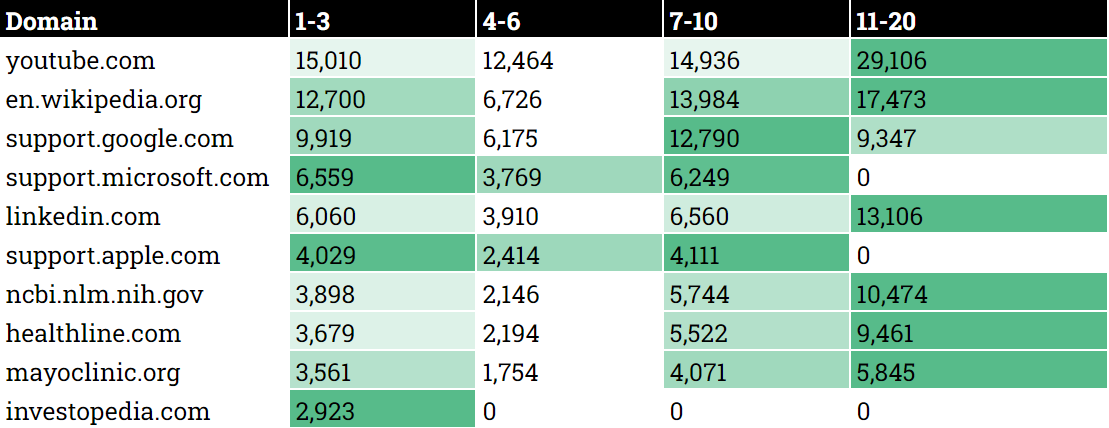 The place the highest 20 domains which might be seen in AIOs and search outcomes rank (Picture Credit score: Kevin Indig)
The place the highest 20 domains which might be seen in AIOs and search outcomes rank (Picture Credit score: Kevin Indig)Situations
I’ll work with my shoppers to match the AIO’s consumer intent, present distinctive insights, and tailor the format. I see choices for the progress of AI Overview that I’ll monitor and validate with knowledge within the subsequent months and years.
Choice 1: AIOs rely extra on top-ranking natural outcomes and fulfill extra informational intent earlier than customers have to click on by way of to web sites. Nearly all of clicks touchdown on websites could be from customers contemplating or intending to purchase.
Choice 2: AIOs proceed to supply solutions from diversified outcomes and depart a small probability that customers nonetheless click on by way of to top-ranking outcomes, albeit in a lot smaller quantities.
Which situation are you betting on?
Featured Picture: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal





