So that you’ve realized a revenue in your investments? Buckle up and prepare to report your transactions to the Inner Income Service (IRS) on Schedule D and see how a lot tax you owe.
However it’s not all unhealthy information. In the event you misplaced cash, this way helps you employ these losses to offset any features or a portion of your atypical earnings, decreasing the taxes you owe. And in the event you profited out of your transactions, Schedule D helps make sure you don’t overpay Uncle Sam on your features.
What’s a Schedule D?
Schedule D is an IRS tax kind that studies your realized features and losses from capital property, that’s, investments and different enterprise pursuits. It consists of related data akin to the full buy value of property, the full value these property have been bought for and whether or not these property have been held for the long run (greater than a yr) or brief time period (lower than a yr).
Who has to file a Schedule D?
You’ll need to file a Schedule D kind in the event you realized any capital features or losses out of your investments in taxable accounts. That’s, in the event you bought an asset in a taxable account, you’ll have to file. Investments embrace shares, ETFs, mutual funds, bonds, choices, actual property, futures, cryptocurrency and extra. Those that have capital losses that they’re carrying over from earlier tax years will wish to file Schedule D in order that they will make the most of the tax profit.
Others might want to file Schedule D as properly. Those that have realized capital features or losses from a partnership, property, belief or S company might want to report these to the IRS on this way. These with features or losses not reported on one other kind can report them on Schedule D, as can filers with nonbusiness unhealthy money owed. These with like-kind exchanges and installment gross sales could have to reply questions on their transactions on Schedule D.
The way you report a achieve or loss and the way you’re taxed
The 2-page Schedule D, with all its sections, columns and particular computations, seems to be daunting and it actually may be.
To start out you need to report any transactions first on Type 8949 after which switch the information to Schedule D. On Type 8949 you’ll word while you purchased the asset and while you bought it, in addition to what it value and what you bought it for. Your buy and gross sales dates are vital as a result of how lengthy you maintain the property determines its tax fee.
In the event you owned the asset for a yr or much less, any achieve would usually value you extra in taxes. These short-term gross sales are taxed on the identical fee as your common earnings, which may very well be as excessive as 37 % in your 2023 tax return. Quick-term gross sales are reported in Half 1 of the shape.
Nonetheless, in the event you held the property for greater than a yr, it’s thought-about a long-term asset and is eligible for a decrease capital features tax fee — 0 %, 15 % or 20 %, relying upon your earnings stage. Gross sales of long-term property are reported in Half 2 of the shape, which seems to be practically similar to Half 1 above.
Element your transactions
As soon as you establish whether or not your achieve or loss is short-term or long-term, it’s time to enter the transaction specifics within the applicable part of Type 8949. All transactions require the identical data, entered in both Half 1 (brief time period) or Half 2 (long run), within the applicable alphabetically designated column. For many transactions, you’ll full:
(a) The identify or description of the asset you bought
(b) Whenever you acquired it
(c) Whenever you bought it
(d) What value you bought it for
(e) The asset’s value or different foundation
(h) The achieve or loss
Complete your entries on Type 8949 after which switch the knowledge to the suitable short-term or long-term sections of Schedule D. On that tax schedule you’ll subtract your foundation from the gross sales value to reach at your whole capital achieve or loss, as within the pattern under.
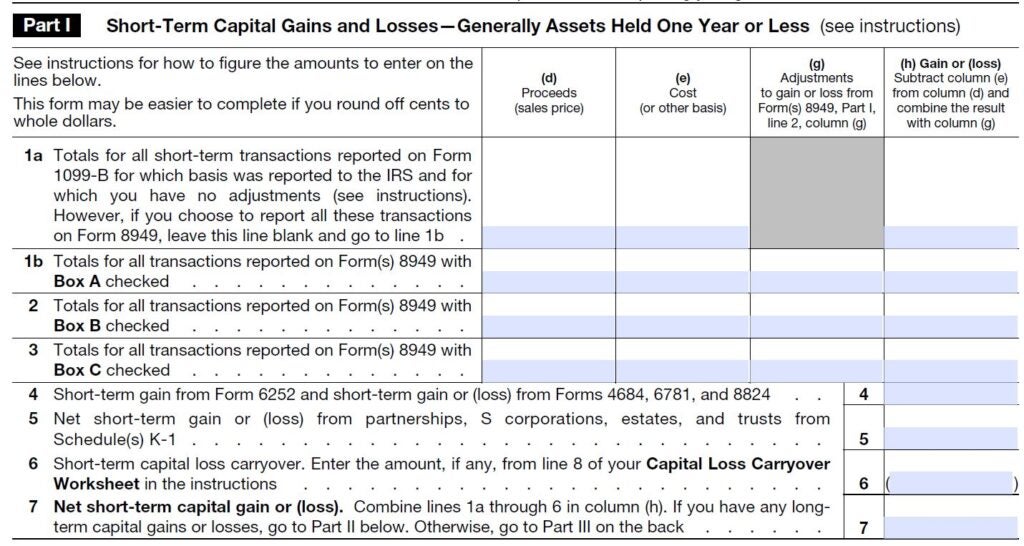
Schedule D additionally asks for data on some particular transactions that don’t apply to all taxpayers, akin to installment gross sales, like-kind exchanges, commodity straddles, gross sales of enterprise property and features or losses reported to you on Schedule Ok-1.
Try the entire record and if any of those apply to your tax state of affairs, it most likely could be sensible to show Schedule D and the remainder of your tax paperwork over to an expert. These are difficult issues, and it may be straightforward to make a mistake even with the very best intentions.
Schedule D additionally requires data on any capital loss carry-over you might have from earlier tax years on line 14, in addition to the quantity of capital features distributions you earned in your investments.
You could possibly keep away from submitting Schedule D, if one of many two conditions under applies to your return:
- If distributions, line 13, are your solely funding gadgets to report, you don’t need to fill out Schedule D; they go immediately in your 1040 or 1040A return.
- You can also escape Schedule D in case your solely capital achieve is from the sale of your residence. So long as you meet some primary residency necessities and your home-sale revenue is $250,000 or much less ($500,000 for married-filing-jointly house sellers), it’s not taxable and also you don’t have to inform the IRS about it right here or on another kind.
Complete your transactions
When you’ve stuffed in all of the short-term and long-term transaction data in Components 1 and a couple of, it’s time to show over Schedule D and mix your asset-sale particulars in Half 3. This part basically consolidates the work you probably did earlier, but it surely’s not as straightforward as merely transferring numbers from the entrance of the schedule to the again.
Strains 16 by means of 22 direct you to different traces and types relying on whether or not your calculations lead to an total achieve or loss. A few traces in Half 3 additionally take care of particular charges for collectibles and depreciated actual property. Once more, in these conditions, professional tax recommendation may be warranted.
Use Schedule D to whole up your features and losses. In the event you whole up a internet capital loss, it’s not good investing information, however it’s good tax information. Your loss can offset your common earnings, decreasing the taxes you owe – as much as a internet $3,000 loss restrict.
In the event you reported a internet loss higher than the annual restrict, it may be carried ahead to make use of in opposition to features in future tax years till it’s exhausted.
As a bonus, your capital loss means you’re by means of with Schedule D. You merely switch your loss quantity to your 1040 and proceed your submitting work there.
Determine the tax in your features
Whenever you provide you with a achieve, the tax paperwork continues. And that is the place the mathematics actually begins, particularly in the event you’re doing all of your taxes by hand as a substitute of utilizing software program.
Relying in your solutions to the assorted Schedule D questions, you’re directed to the separate Certified Dividends and Capital Achieve Tax worksheet or the Schedule D Tax worksheet, that are discovered within the Type 1040 directions booklet. These worksheets take you thru calculations of your varied sorts of earnings and determine the suitable taxation stage for every.
Earlier than you start both of those worksheets, ensure you’ve accomplished your Type 1040 by means of line 11 (that’s your taxable earnings quantity), as a result of that’s the start line of each worksheets. From there you’ll have numerous addition, subtraction, multiplication and transferring of numbers from varied types.
However in the event you bought inventory or different property, don’t be tempted to disregard Type 8949, Schedule D, the related tax worksheets and all the additional calculations. Keep in mind, the IRS acquired a replica of any tax assertion your dealer despatched you, so the company is anticipating you to element the sale, and achieve or loss, together with your tax submitting.
Backside line
The additional work wanted in figuring your capital features taxes is usually to your benefit. Common earnings tax charges may be greater than twice what’s levied on some long-term capital features. So while you’re lastly by means of with the calculations, your tax invoice ought to be decrease than it will have been in the event you had merely used the usual tax desk to seek out your tax due.
Word: Kay Bell contributed to a earlier model of this story.





